|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
|
|
|
Welcome
Updating to Mascot Server 3.1 can easily give 50% more peptide identifications in Thermo Proteome Discoverer.
This month's highlighted publication reveals how maternal immune activation imprints translational dysregulation in descendant neural stem cells.
We presented a poster at US HUPO 2025 describing Mascot's customizable machine learning adapter framework.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Mascot: The trusted reference standard for protein identification by mass spectrometry for 25 years
|
Get a quote
|
 |
|
|
|
Using machine learning with Mascot and Proteome Discoverer
|
|
|
Thermo Proteome Discoverer (PD) has a built-in node that integrates with Mascot Server, which supports all versions from Mascot Server 2.0 to the latest 3.x.
However, the Mascot node does not currently have a user interface for selecting a DeepLC (predicted retention times) or MS2PIP model (predicted fragment intensities).
With Mascot Server 3.1, you can now define these parameters in the Mascot instrument editor.
When you submit the search using the new 'instrument', Mascot automatically runs MS2Rescore, refines the results with Percolator and exports the refined results into PD.
The integration works with all versions of PD (1.4, 2.x, 3.x) and requires no software changes.
To illustrate, we processed a QC DDA run from a benchmark data set (PXD028735) in PD 3.1 and PD 2.4.
The raw data were acquired on Thermo Orbitrap QE HF-X using HCD.
We configured a Mascot instrument "MS2PIP:HCD2021", which selects the MS2PIP model HCD2021 for fragment intensities.
In PD 3.1, using the MS2PIP:HCD2021 instrument yields 34,141 Peptide Groups, which is almost 60% more than without machine learning.
In PD 2.4, the same settings produce 35,047 Peptide Groups, which is over 100% more.
The relatively bigger jump in PD 2.4 is caused by differences in score threshold calculation when machine learning is not enabled.
When machine learning is enabled, the score threshold in both cases is sensible and consistent, and the results are now in line with the Protein Family Summary report viewed in Mascot Server.
Full details are in our blog.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here, please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
Maternal immune activation imprints translational dysregulation and differential MAP2 phosphorylation in descendant neural stem cells
Sandra M. Martín-Guerrero, María Martín-Estebané, Antonio J. Lara Ordóñez, Miguel Cánovas, David Martín-Oliva, Javier González-Maeso, Pedro R. Cutillas & Juan F. López-Giménez
Molecular Psychiatry (2025) doi:10.1038/s41380-025-02905-5
Environmental stressors such as viral infections can induce maternal immune activation (MIA) during pregnancy, which affects the normal development of the central nervous system in the offspring.
In humans, the process has been linked to the development of neuropsychiatric conditions.
To elucidate the mechanism, the authors cultured neural stem cell (NSC) lines from fetuses carried by pregnant mice.
These were treated with polyinosinic : polycytidylic acid or Poly (I:C), which is a synthetic analog of double-stranded RNA and can mimic the acute phase of viral infection.
Control cases were treated with saline.
The samples were subjected to transcriptomic, proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses.
For proteomics and phosphoproteomics by LC-MS/MS, they used Mascot Distiller for generating peak lists from raw data and Mascot Server for identifying peptides.
The steps were automated with Mascot Daemon, and followed by LFQ using Pescal.
Several differences in protein expression patterns were found between differentiated Poly (I:C) NSCs and saline NSCs,
and significant differences were found in the basal phosphoproteomics profile.
Interestingly, these were not apparent in transcriptomics data.
Most of the proteins displaying differential phosphorylation are related to cytoskeleton structure, involved in neuronal projections.
In particular, the authors identified 52 distinct microtubule-associated MAP2 phosphopeptides, where 17 were elevated in Poly (I:C) compared to saline.
The authors note that hyperphosphorylation of MAP2 is consistent with postmortem brain samples from individuals with schizophrenia, as well as other animal models.
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Customizable ML adapter framework
|
|
|
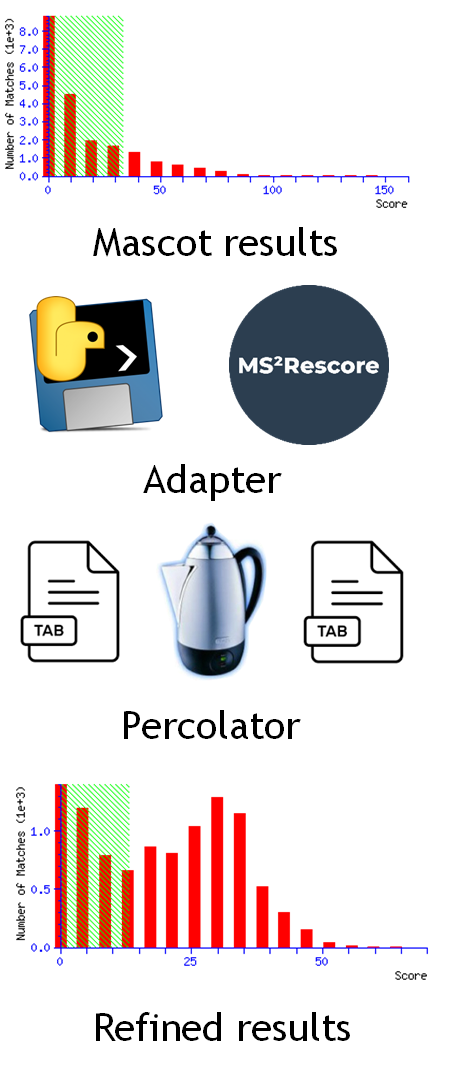
Mascot Server 3.0 introduced a customizable framework for machine learning adapters.
The adapter is a standalone program that accepts a Mascot results file and a CSV specification file as input.
It can perform any computations necessary or call external utilities.
Then, the output of the adapter is a CSV table of computed or predicted features for each peptide match, which Mascot merges with core features in the Percolator input file.
Finally, Mascot runs Percolator to rescore the results.
We used this adapter framework to integrate MS2Rescore with Mascot, but it can be used to integrate any ML predictor.
Check out our US HUPO 2025 poster for more details.
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot continues to be cited by over 2000 publications every year. Our software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Get a quote
|
|
|
You can also contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|





|
|
|
|
|