|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
 |
|
Welcome
We discuss mzTab, the PSI's lightweight interchange format for search results.
This month's highlighted publication shows an improved method for investigating the immunopeptidome from low cell numbers.
If you have a recent publication that you would like us to consider for an upcoming Newsletter, please
send us a PDF or a URL.
Mascot tip of the month is a reminder that you can search negative ion data as easily as positive.
Please have a read and feel free to contact us if you have any comments or questions. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
HUPO 2016, Taiwan
Matrix Science will be exhibiting at the upcoming 15th Human Proteome Organization World Congress (HUPO 2016) to be held in Taipei, Taiwan from September 18th to the 22nd.
We invite you to stop by booth number 23 with your questions about Mascot Server and Mascot Distiller - or just to say Hello! |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Export in mzTab format
Mascot Server can export search results in a wide range of formats, the latest addition being mzTab, the new lightweight format developed by the Proteomics Standards Initiative.
mzTab shares the same controlled vocabulary with mzIdentML, but is table-based, not XML, and can contain both identification and quantitation data. Unlike mzIdentML, an mzTab table is ideal for pasting into a spreadsheet.
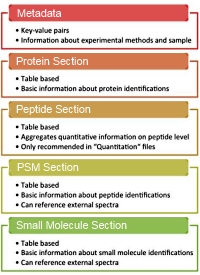
The file starts with a metadata section, followed by four optional sections: one table for each of proteins, peptide-spectrum matches, peptides and small molecules. Additionally there are two main types of files, Identification and Quantification, and two modes, Summary and Complete. mzTab also supports combining results from multiple search engines.
Mascot Server 2.5 is the first search engine to offer native mzTab exporting and supports both Identification and Quantification mzTab files. Go here to read more about implementing mzTab exports. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
Approach for identifying HLA-DR bound peptides from scarce clinical samples
Tina Heyder, Maxie Kohler, Nataliya K. Tarasova, Sabrina Haag, Dorothea Rutishauser, Natalia V Rivera, Charlotta Sandin, Sohel Mia, Vivianne Malmstrom, Asa M. Wheelock, Jan Wahlstrom, Rikard Holmdahl, Anders Eklund, Roman A. Zubarev, Johan Grunewald and Anders Jimmy Ytterberg
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (2016) published online July 24, 2016
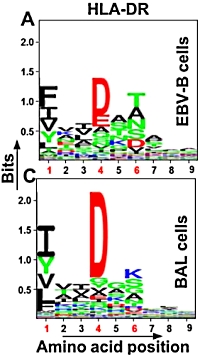
In the field of immunopeptidomics, large numbers of cells are often required due to the complexity of the samples and the limitations of the methods. Here the authors have developed an improved method for the identification of HLA-DR bound peptides from low cell numbers.
The authors used cell populations consisting of Epstein-Barr-immortalized B cells and broncoalveolar lavage cells obtained from patients with sarcoidosis. The optimized approach included cell lysis, immunoprecipitation of HLA-DR, elution of HLA-DR bound peptides, desalting and peptide concentration, and identification by mass spectrometry followed by peptide filtering.
This resulted in the identification of 507 peptides (from 75 proteins) in the EBV-B cells and 1,434 peptides (from 215 proteins) in the BAL samples with an average yield of 10.1 peptides/million cells. This yield represents a 1 to 2 order of magnitude improvement over previous studies. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Mascot tip of the month
Support for negative ion data was added to Mascot Server in version 2.1, way back in 2005. We suspect that it was little used at the time, but there are signs that negative ion mode may be gaining wider interest, particularly in connection with photodissociation.
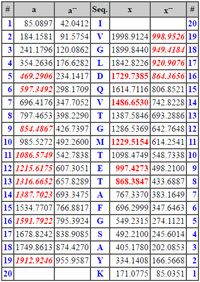
As long as your instrument data system or peak picking software is capable of creating a peak list which specifies negative charges, searching negative ion data is no different to searching positive. That is, the charge line in the MGF peak list needs to read CHARGE=2- rather than CHARGE=2+, etc. If this is a problem, you can always use Mascot Distiller.
For some types of data, you may need to create a new instrument type. In negative ETD, the major ion series are a-type, where the charge is from gaining an electron rather than losing a proton, and x-type, which are standard Mascot x ions. The a-type can be simulated by including Mascot a ions in the instrument and a fixed N-term modification of zero mass, e.g. C H(6) N(-7) O(5), and a neutral loss of H(-1). |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Please contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|
 |
 |
|
|