|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
 |
|
Welcome
Please join us for our annual ASMS User Meetings in Atlanta on June 3rd and 4th.
Mascot Daemon, included with the Mascot Server license, is a powerful ally in increasing lab efficiency.
This month's highlighted publication shows a new method for the isolation and identification of protein C-termini.
If you have a recent publication that you would like us to consider for an upcoming Newsletter, please
send us a PDF or a URL.
Mascot tip of the month lists Mascot Distiller settings that have a major influence on quantitation speed.
Please have a read and feel free to contact us if you have any comments or questions. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Matrix Science ASMS User Meetings
Join us for breakfast and learn about exciting applications of database searching as well as how to get the most out of Mascot.
There is no charge for attending these meetings, but advance registration is required. Breakfast will be provided.
Monday 3 June, 7:00 am - 8:00 am
Database searching in systems without a genome: lessons learned with the California sea lion
presented by Ben Neely, Marine Biochemical Sciences Group, NIST
Metaproteomics with Mascot
presented by Matrix Science
Tuesday 4 June, 7:00 am - 8:00 am
A day in the life of a database search engine: Mascot as robust and scalable tool for protein identification in a contract research environment
presented by Michael Ford, MS Bioworks
Trypsin isn't the only protease: Processing and searching middle down datasets with Mascot Distiller and Mascot Server
presented by Matrix Science
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Mascot Daemon - the key to automation
Mascot Daemon can readily automate the processing of raw data, submit multiple searches, direct quantitation, and perform a combination of tasks.
By linking together a number of follow-up tasks, Daemon will take the data used in one task and re-search it with a different set of conditions. Examples include identifying and removing matches from a search against a contaminants database prior to searching the main database or searching both spectral libraries and protein or DNA sequence databases.
Daemon does more than just automate the peak picking and searching. For instance, with quantitation data, Daemon can automatically calculate and export the quantitation results. It can also trigger a program that performs a task after every search is complete such as sending an email or importing results into a lab database.
And if you are in a multi-user or core lab, you can run searches on behalf of your customers or collaborators so that they can view their results but not rerun the search.
Go here to learn more about putting Daemon to work for you.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
In-depth Analysis of C Terminome Based on LysC Digestion and Site-selective Dimethylation
Xiaoxian Du, Caiyun Fang, Lijun Yang, Huimin Bao, Lei Zhang, Guoquan Yan, and Haojie Lu
Anal. Chem., Published online April 26, 2019
Protein C termini play an important role in a variety of biological functions such as protein sorting, protein activity, and formation of protein complexes. Additionally, sequence tags at C termini have very high specificity for protein identification.
The authors have developed a method for the isolation and identification of protein C-termini using LysC digestion followed by site-selective dimethylation:
- Protein samples were digested into peptides by endoproteinase LysC
- All α-amines of the LysC digest were blocked by site-selective dimethylation
- Benefiting from the free ε-amines of lysine residues, N-terminal and internal peptides containing lysine residue were selectively removed by covalently binding to AminoLink resin.
- The enriched sample was analyzed by LC-MS/MS and database searching
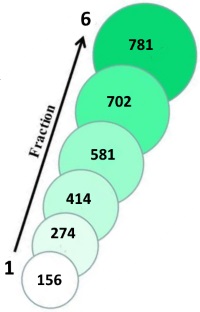
Using this method, they identified 781 protein C termini from 300 μg of HeLa cell proteins. They also constructed a peptide-centric database which was composed of theoretically identifiable C-terminal peptides obtained by in silico LysC digestion of the human proteome.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Mascot Tip
When using Mascot Distiller for quantitation, there are some choices that can have a big impact on total processing time.
General
- Distiller updates are free, so make sure you are using 2.7 or later, which has much faster peak picking for many file formats
- Distiller uses all the processor cores it can find, so install Distiller on a PC with lots of fast cores
- If it is a large data set, it will be time efficient to optimise settings on one or two raw files.
Processing options
- Are the MS2 scans saved as centroids? If so, use settings that take the existing centroid masses. Repeating the peak picking is unlikely to make much difference to protein quantitation
- Don't look for very high values of precursor charge that aren't in the data. Peak pick a few survey scans at random and see what range of charge states will cover the bulk of strong precursors
Database search
- Specify an absolute minimum of variable modifications. No point matching peptides that aren't representative of protein abundance
- Search a database for the target organism plus contaminants or cRAP. In most cases, the relevant UniProt proteome is the right choice
Quantitation
- If you want to experiment with some settings, you can quantify just one or two proteins to save time
- If the method has all charge states checked, turn it off. It rarely improves things
- Leave normalisation turned off until you are ready to quantify the complete data set
- For replicate protocol, estimate the worst case difference in elution times from features in the TICs and set the limit on elution time difference to a slightly greater value
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Please contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|
 |
 |
|
|