|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
 |
|
Welcome
Easily create a myriad of powerful charts and plots from your quantitation results.
This month's highlighted publication describes how the authors stimulated synaptic proteins and quantified the sialylation, potentially showing a new mode of neural communication.
If you have a recent publication that you would like us to consider for an upcoming Newsletter, please
send us a PDF or a URL.
Mascot tip of the month explains the differences between custom and predefined configurations in Mascot Server Database Manager.
Please have a read and feel free to contact us if you have any comments or questions. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
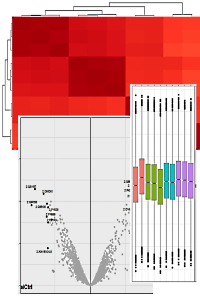
Creating Charts and Plots from the Quantitation Summary
Once you have your expression data compiled into a Quantitation Summary, data analysis and visualization can proceed using a variety of powerful third-party software tools. This simplest is to manipulate the data within Excel, though this is somewhat limited, while the Perseus application offers a range to tools with a graphical user interface. For an even greater array of tools, Bioconductor offers over 200 scripts for proteomics and mass spectrometry data analysis.
To illustrate what can be achieved with a few lines of R script, we examined a 10-plex TMT data set of oncogenic microRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer. Box plots, PCA clustering, heatmap relationships, and a volcano plot for fold changes are readily produced.
To get you started, the Sample Map and Quantitation Summary are well documented in the Mascot Daemon help file, and Bioconductor has extensive support and tutorial material.
Please go here to read the details.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
Depolarization-dependent induction of site-specific changes in sialylation on N-linked glycoproteins in rat nerve terminals
Inga Boll, Pia Jensen, Veit Schwaemmle and Martin R. Larsen
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 19, 1418-1435 (2020)
The authors investigated sialylation on the N-linked glycosylation of synaptic proteins isolated from rat brain nerve terminals. Using TiO2 chromatography in combination with enzymatic deglycosylation, TMT quantification, and LC-MS/MS, they identified over 5000 proteins.
The cells were also stimulated for 5 sec. with KCl, with this depolarization led to a variety of sialylation and desialylation events. The authors found that the abundances of 430 glycosites changed after five seconds depolarization. From this they proposed that sialylation is a dynamic PTM that could have significant influence on the synaptic transmission processes in nerve terminals.
They also screened the proteomics data to identify enzymes that might be responsible for sialylation and desialylation, finding 3 sialidases and 8 sialyltransferases.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Mascot Tip
Mascot Server Database Manager offers two types of database definition: custom and predefined. Custom is easily described and understood. You, the user, specify all aspects of the configuration, such as download URL and parse rules. You can use an existing definition as a template, or start from scratch.
Predefined means that Matrix Science has specified the configuration, and only limited changes are possible. If the database you want to add is predefined, using this rather than a custom definition has several advantages:
- Up and running with a few mouse clicks
- A reliable and tested configuration
- Matrix Science keeps the definition up-to-date
The last point means that if something changes, such as the download URL or the title line format, we update the definition so that it is correct next time you want to update your local database files. We also recommend choosing predefined for any database that uses taxonomy files, because this makes a custom definition more complicated.
Either type of definition may or may not be set for automatic updates. The only requirement to enable automatic updates is that the definition specifies download URLs for all of the required files. All predefined definitions will have download URLs, but this is optional for a custom definition.
More information on the Database Manager help page.
|

|
 |
 |
 |
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Please contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|
 |
 |
|
|