|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
 |
|
Welcome
Please join us for our annual ASMS User Meeting in Minneapolis on June 6th.
The NCBI nr database can be useful, but care is needed when dealing with the huge Fasta file.
This month's highlighted publication gives a new method for high throughput and reproducible protein sample preparation.
If you have a recent publication that you would like us to consider for an upcoming Newsletter, please
send us a PDF or a URL.
Mascot tip of the month covers the fixes in the latest Mascot Server patch.
Please have a read and feel free to contact us if you have any comments or questions. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Matrix Science ASMS User Meeting
Join us for breakfast at ASMS in Minneapolis and learn about the exciting applications of database searching as well as how to get the most out of Mascot.
There is no charge for attending this meeting, but advance registration is required. Breakfast will be provided.
Monday 6 June, 7:00 am - 8:00 am
Identification and Quantification of Histone Methylation in Cancer Cells
presented by Dr Roland Annan, GlaxoSmithKline
NCBIprot, mzIdentML 1.2 and other improvements in Mascot Server 2.8.1
presented by Ville Koskinen, Matrix Science
Fractionated LFQ in Mascot Distiller 2.8.2
presented by Patrick Emery, Matrix Science
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Best approaches for using the NCBI nr database
The NCBI nr database contains a comprehensive set of non-redundant protein sequences and is frequently updated. However, due to its huge size (in July 2021, the 190 GB Fasta file contained 409 million entries) it should usually be a database of last resort. When you do need to use it, we have a few suggestions to help you be successful.
- Hardware: Compressing the database tends to be limited by disk throughput and random-access speed so we recommend using a RAID10 array or a data center grade NVMe or SSD disk. You need to have at least 800 GB of free disk space for the database and associated files.
- Bringing the database online: This is an automated process, and how long this takes depends on the disk performance. If you get an error that the test search has timed out, simply increase the value of MonitorTestTimeout in mascot.dat Options section.
- Searching: The key to searching NCBI nr is choosing a narrow taxonomy filter. Searching the whole database will not only take a long time, but you'll also lose sensitivity.
To read more details about successfully using NCBI nr, Go here. (Note that the pre-defined URL for downloading the Fasta has been updated to HTTPS protocol, so that the note in the blog article about the limitation of FTP and using rsync no longer applies.)
|

|
 |
 |
 |
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
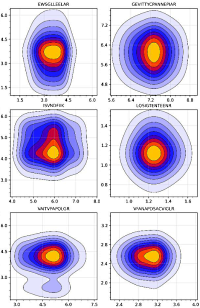
Toward Zero Variance in Proteomics Sample Preparation: Positive-Pressure FASP in 96-Well Format (PF96) Enables Highly Reproducible, Time- and Cost-Efficient Analysis of Sample Cohorts
Stefan Loroch, Dominik Kopczynski, Adriana C. Schneider, Cornelia Schumbrutzki, Ingo Feldmann, Eleftherios Panagiotidis, Yvonne Reinders, Roman Sakson, Fiorella A. Solari, Alicia Vening, Frauke Swieringa, Johan W. M. Heemskerk, Maria Grandoch, Thomas Dandekar, and Albert Sickmann
J. Proteome Res., 21 1181-1188 (2022)
The authors developed a new approach (PF96) to address the common bottleneck of sample preparation and processing when larger sample sets are being investigated. They utilized a positive-pressure-based molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) filter membrane in 96-well format in concert with a commercial solid-phase extraction unit.
First, samples are transferred to a 96-well plate, reduced and alkylated, and then loaded onto a 96-well 30 kDa MWCO filter plate. Next, liquids are forced through the filter by positive pressure, and buffers are added by automatic dispensing followed by enzymatic digestion. Third, peptides are recovered by positive pressure into another 96-well plate, and aliquots for LC-MS analysis are transferred to 96-well glass vial plates.
The authors performed DDA analysis of HeLa cell and mouse heart tissue lysates, loading from 3 to 60 µg total protein onto the filters and obtained excellent reproducibility across the range. They further tested the approach with 48 µg of mouse heart tissue lysate processed in 40 technical replicates. They evaluated the results with (1) Pearson correlation in DDA, (2) quantification of 16 endogenous peptides (spanning 104 in abundance) by targeted LC-MS, and (3) quantification of the same 16 endogenous peptides against stable-isotope-labeled reference peptides by targeted LC-MS. They concluded that the PF96 method provides only a minor and barely assessable contribution to the overall variance of proteomics analyses, while increasing throughput five-fold.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Please contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|
 |
 |
|
|