|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
|
|
|
Welcome
We have tutorials and resources for all the basic steps of the LC-MS/MS workflow.
In this month's highlighted publication, the authors unravel some of the complexity of histone variants and PTMs.
Is your Mascot computer aging? Moving to new hardware is straightforward, and we can provide a free 14-day temporary licence for the transition.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Mascot: The trusted reference standard for protein identification by mass spectrometry for 25 years
|
Get a quote
|
 |
|
|
|
Mascot workflow for LC-MS/MS
|
|
|
Whether you are new to mass spectrometry proteomics or a seasoned expert, it's beneficial to periodically take a step back and look at the basics.
We have compiled a summary of the Mascot workflow for LC-MS/MS and paired it with resources that can help you optimize your work.
Every workflow starts from raw data. We have tools and tips for configuring Mascot Distiller peak picking options, enabling chimeric DDA processing and experimenting with narrow window DIA.
Several tutorials on our website cover different aspects of database searching, like how to optimize your search parameters, what the peptide-spectrum match statistics mean and rescoring target-decoy results using Percolator.
In most experiments, the goal is to not only identify proteins but also quantify the relative amounts across samples.
We have a number of tutorials to help with understanding quantitation statistics, reporting quantitation datasets or employing one of the many supported protocols.
Read more about these resources in our blog.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here, please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
Histone chaperone deficiency in Arabidopsis plants triggers adaptive epigenetic changes in histone variants and modifications
Michal Franek, Martina Nešpor Dadejová, Pavlína Pírek, Karolína Kryštofová, Tereza Dobisová, Zbyněk Zdráhal, Martina Dvořáčková, Gabriela Lochmanová
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, published online: June 05, 2024
The authors used MS-based approaches to explore how different epigenetic factors interact in Arabidopsis mutants lacking certain histone chaperones, elucidating the histone variant ratios and their PTMs. Histones were extracted from wild type and mutant Arabidopsis seedlings, and derivatized with propionic anhydride. Following trypsin digestions, the peptides were further propionylated, then analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The peptides were searched against the UniProtKB Arabidopsis thaliana database as well as an in-house AT-histone database. Variable modifications were acetylation and propionylation for the UniProtKB search, and acetylation, methylation, dimethylation, trimethylation, phosphorylation and propionylation for the histone database. Database search results were further refined using Percolator.
Selected histone peptide identifications were manually verified and quantified from the peak areas derived from the EICs using the Skyline software. The relative abundance of a particular histone sequence subvariant (e.g., H2A.Z, H2A.X, or H2A.W) was calculated as the ratio of the averaged area of the precursor peaks of its unique peptides to the total area of these variants.
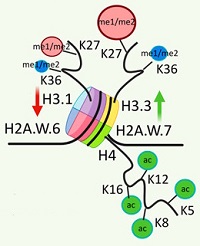
The authors showed that deficiencies in the CAF-1 chaperon lead to changes in the methylation profiles of H3.1 and H3.3 variants. The altered H3.3 incorporation affects the methylation status at K27 and K36 positions, which are important for transcriptional regulation and DNA damage response. Specifically, they found that the K36me1/2/3 is predominant in H3.3 and not easily detected in H3.1 due to the low abundance. And the majority of H3.1K27−R40 peptides were methylated with predominant K27me1. Zeocin treatment induced genotoxic stress and altered the levels of selected histones with the levels of H3.3K27 monomethylated marks in the AT mutant increasing significantly.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Free temp licence when moving to new hardware
|
|
|
When was the last time you installed Mascot Server?
If it has been a few years, it may be time to think about moving to new hardware.
Power efficiency, processor performance, memory capacity and disk speed have all improved significantly in the last five years.
It's also beneficial to migrate well before something breaks, not after the fact.
For example, this year we upgraded matrixscience.com from an aging BladeCenter cluster to a single Intel Xeon Gold server.
The new server uses a lot less energy, because the single processor is as performant as six of the old two-processor blade servers.
Going from a RAID array of mechanical hard disks to NVMe RAID improved system responsiveness.
A single box is also simpler to manage than a cluster of servers.
Migrating is straightforward and the step-by-step instructions are available on our website.
We are happy to assist you before and after migration. Contact us to check your support status or ask for a quote to renew support.
If you want to try Mascot on the new hardware before making the switch, please ask for a free, 14-day temporary licence.
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot continues to be cited by over 2000 publications every year. Our software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Get a quote
|
|
|
You can also contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|




|
|
|
|
|